If you look at a piano a half step above b flat is b natural and one more half step above that is c natural.
Add notes a whole step above.
The distance between the first two notes in a major scale is a whole step.
So it s a whole step from b flat to c natural.
So db is the next key to the left of d.
The only difference is that they have different note names.
Hence the interval between c and d is a diatonic half step.
For example look at the pitches e and f on the keyboard.
C is a c note while d is a d note.
C is a c note while db is a d note.
A tr above the trilled note.
This stands for whole step whole step half step whole step whole step whole step half step.
Tones and semitones in a major scale.
Avoid the temptation to think of a whole step as one letter name to the next letter name.
D also sounds the same as cx since it is a whole step above c.
Those are the two naturally occuring half steps in a major scale.
D also sounds the same as cx since it is a whole tone above c.
However sometimes a composer wants a downward trill or even a half step trill and he or she writes the specific note to be used in the trill in one of several ways.
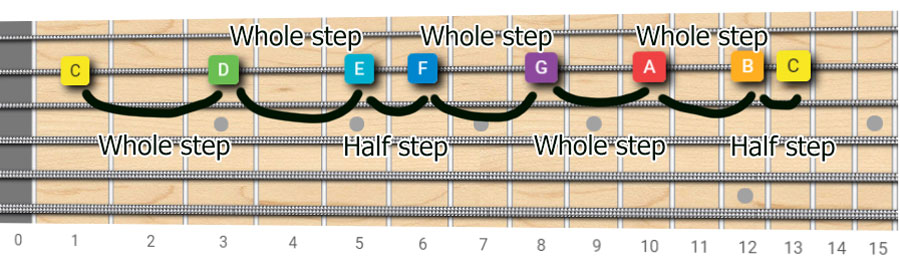
The distance between the 3rd and 4th notes and the 7th and 8th notes are half steps.
Logically enough flats are defined as the note that is one half step lower than the note you are starting on.
To determine the whole step above e count two half steps to the right of that key.
C is a chromatic semitone higher than c and db is a diatonic semitone higher than c.
In western music an octave is broken up into 12 tones called half steps or semitones.
By holly day jerry kovarksy blake neely david pearl michael pilhofer.
Like the whole note it is represented by a hollow oval with double stems on either sides.
A sharp or flat sign which tells you to trill to the note s sharp or to the note s flat.
A half step on the piano is the very next key.
A major scale is formed with the formula w w h w w w h.
Notes greater than a whole note double whole note.
W w h w w w h whole whole half whole whole whole half.
It is the longest note value that is still in use in modern music notation.
While flats and sharps alter a note by a half step the double flat and double sharp alter a note by a whole step.
C natural is a whole step above b flat.
While flats and sharps alter a note by a semitone the double flat and double sharp alter a.
To play the piano or keyboard you should know that a musical scale contains seven notes meaning that some of the distance between notes in a scale spans one half step and some spans at least two half steps.
All major scales follow this exact pattern.
The hence the interval between c and db is a diatonic half step.
There is no black key between them so the interval between e and f is a half step.
Or a sharp or.
So c is the very next key to the right after the c and it happens to be a black key.
Also known as a breve or a double note it is twice as long as a semibreve.